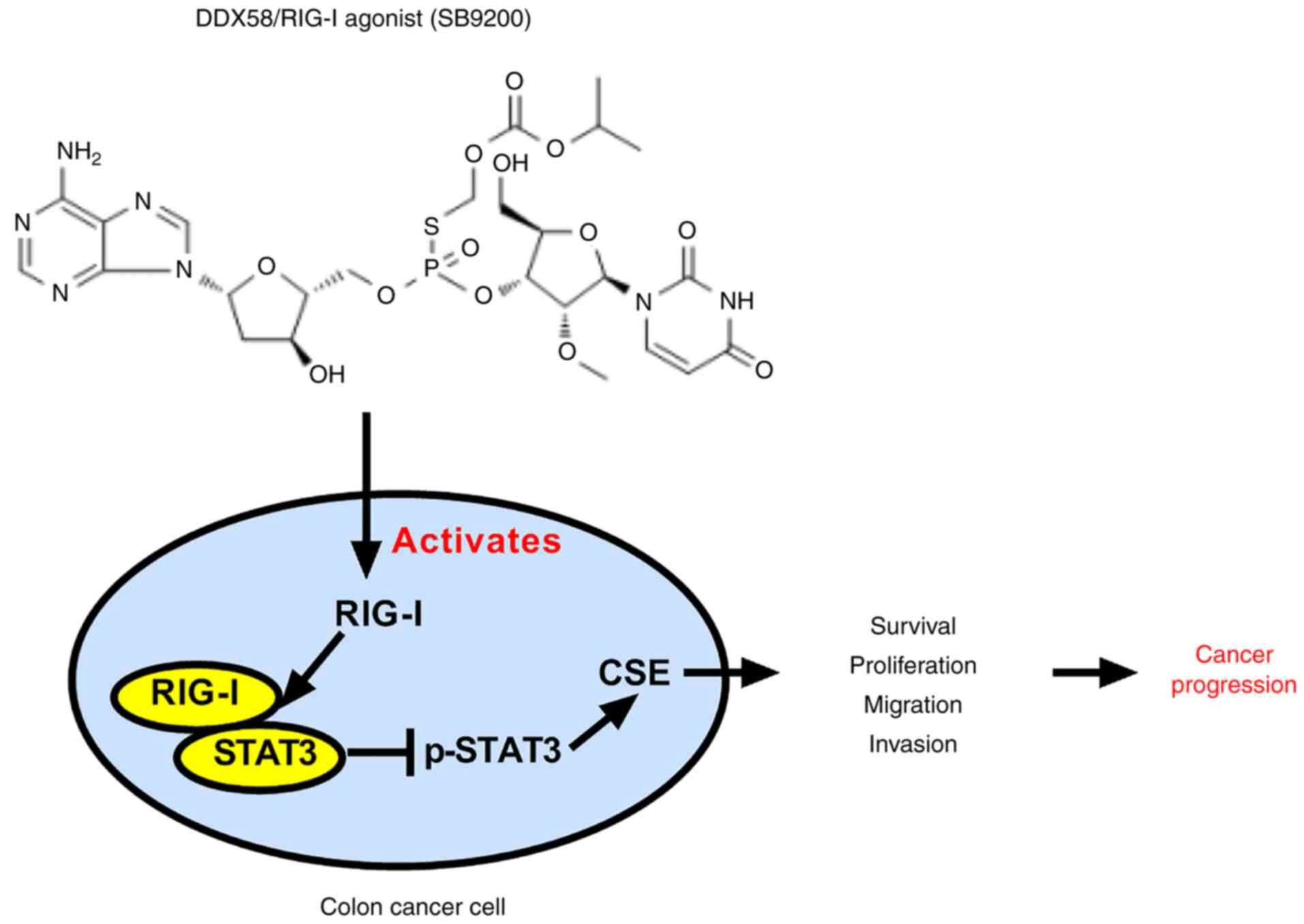
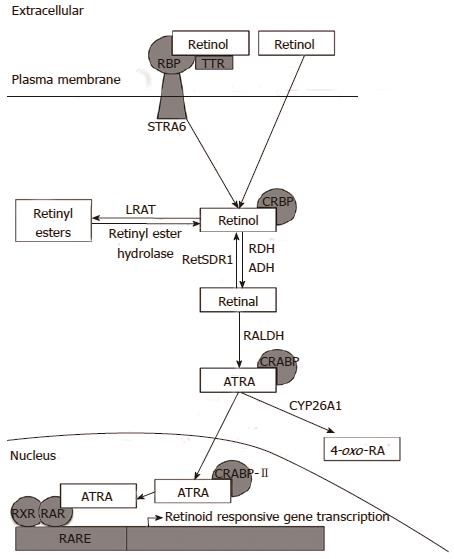
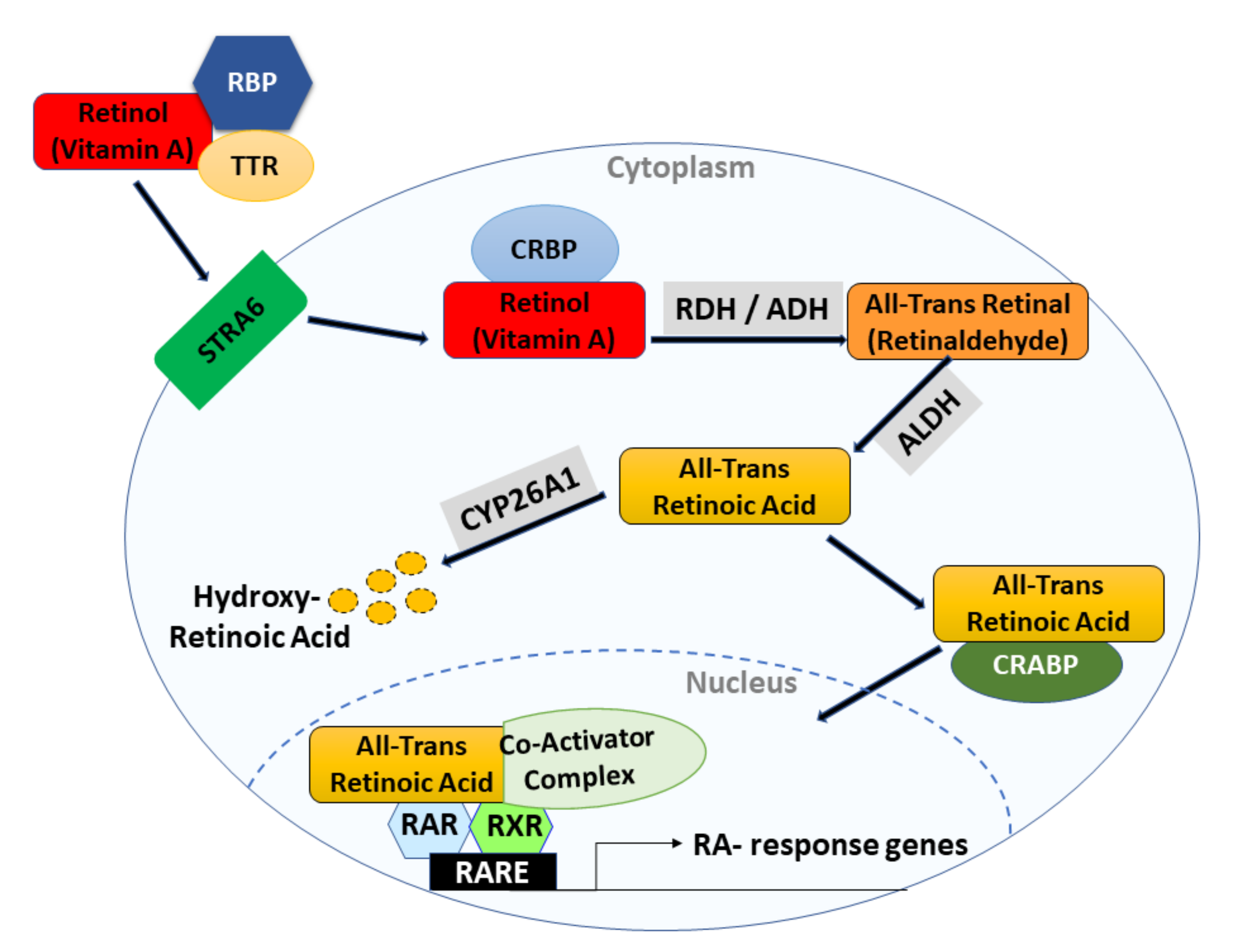
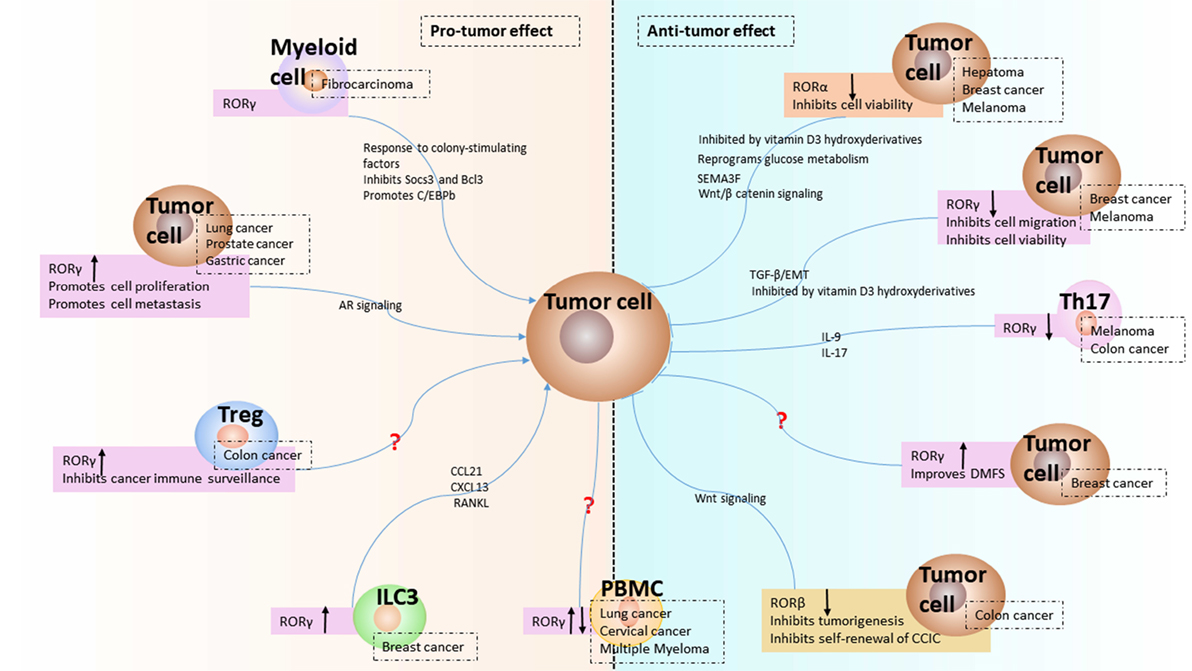
Polyplexes of retinoic acid: an in vitro study of complex nanostructures against colorectal cancer cell line (HCT-15) | SpringerLink
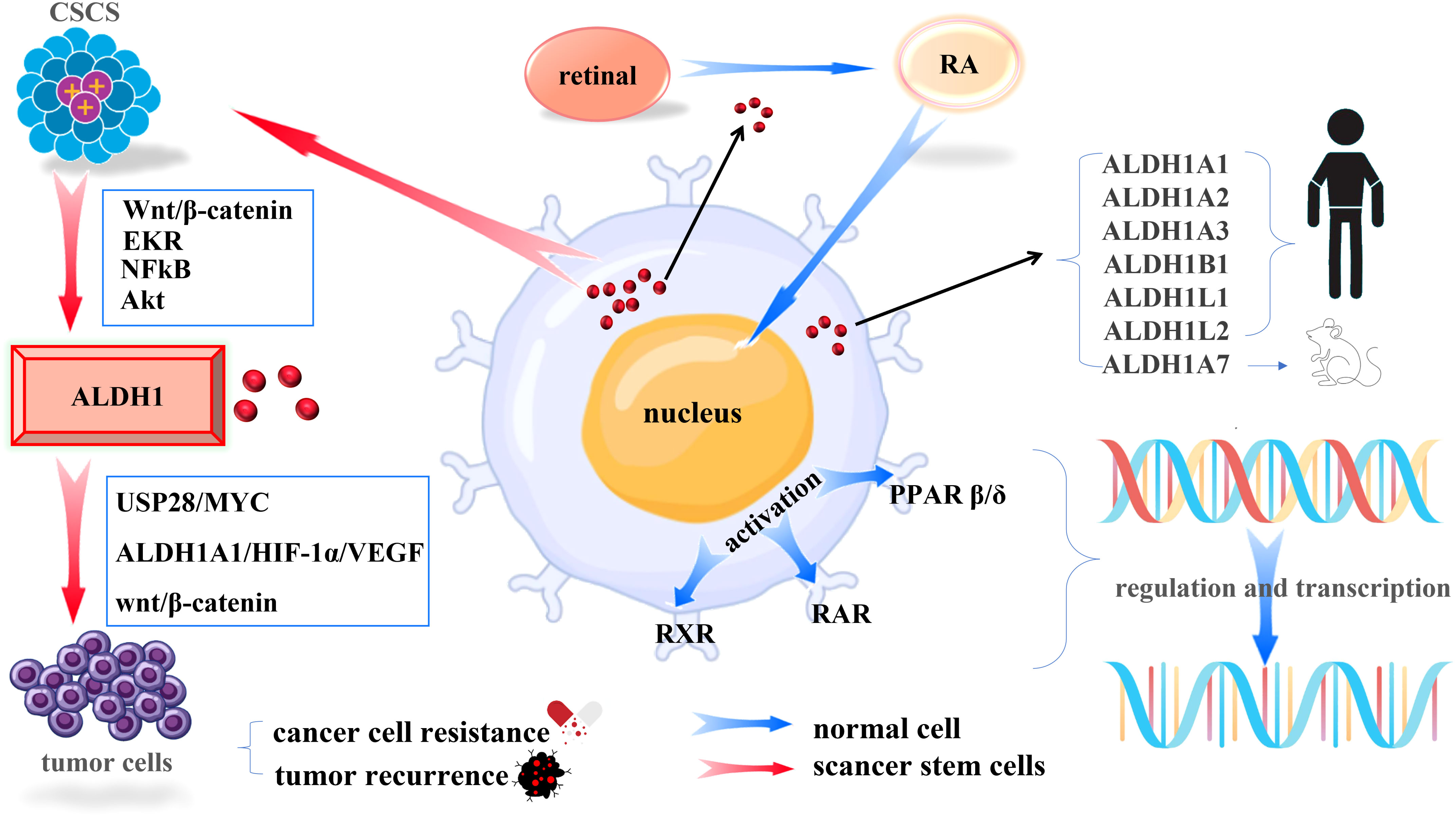
The anti-cancer effect of retinoic acid signaling in CRC occurs via decreased growth of ALDH+ colon cancer stem cells and increased differentiation of stem... | Oncotarget
Normalizing Microbiota-Induced Retinoic Acid Deficiency Stimulates Protective CD8+ T Cell-Mediated Immunity in Colorectal Cancer
The anti-cancer effect of retinoic acid signaling in CRC occurs via decreased growth of ALDH+ colon cancer stem cells and increa

Normalizing Microbiota-Induced Retinoic Acid Deficiency Stimulates Protective CD8(+) T Cell-Mediated Immunity in Colorectal Cancer. | Semantic Scholar

Inhibition of the all-trans Retinoic Acid (atRA) Hydroxylases CYP26A1 and CYP26B1 Results in Dynamic, Tissue-Specific Changes in Endogenous atRA Signaling | Drug Metabolism & Disposition

Retinol inhibits the growth of ATRA-resistant human colon cancer cells.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | Two Opposing Faces of Retinoic Acid: Induction of Stemness or Induction of Differentiation Depending on Cell-Type