Inactivation of LL-37 during the interplay between C. albicans cells... | Download Scientific Diagram
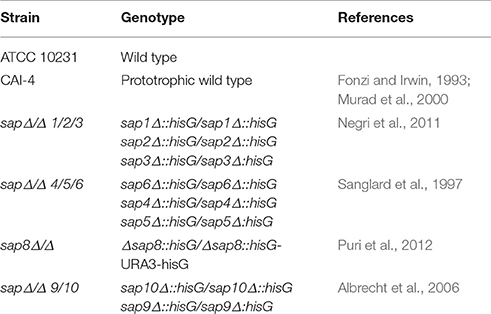
Frontiers | Aspartic Proteases and Major Cell Wall Components in Candida albicans Trigger the Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps

Global Secretome Characterization of the Pathogenic Yeast Candida glabrata | Journal of Proteome Research

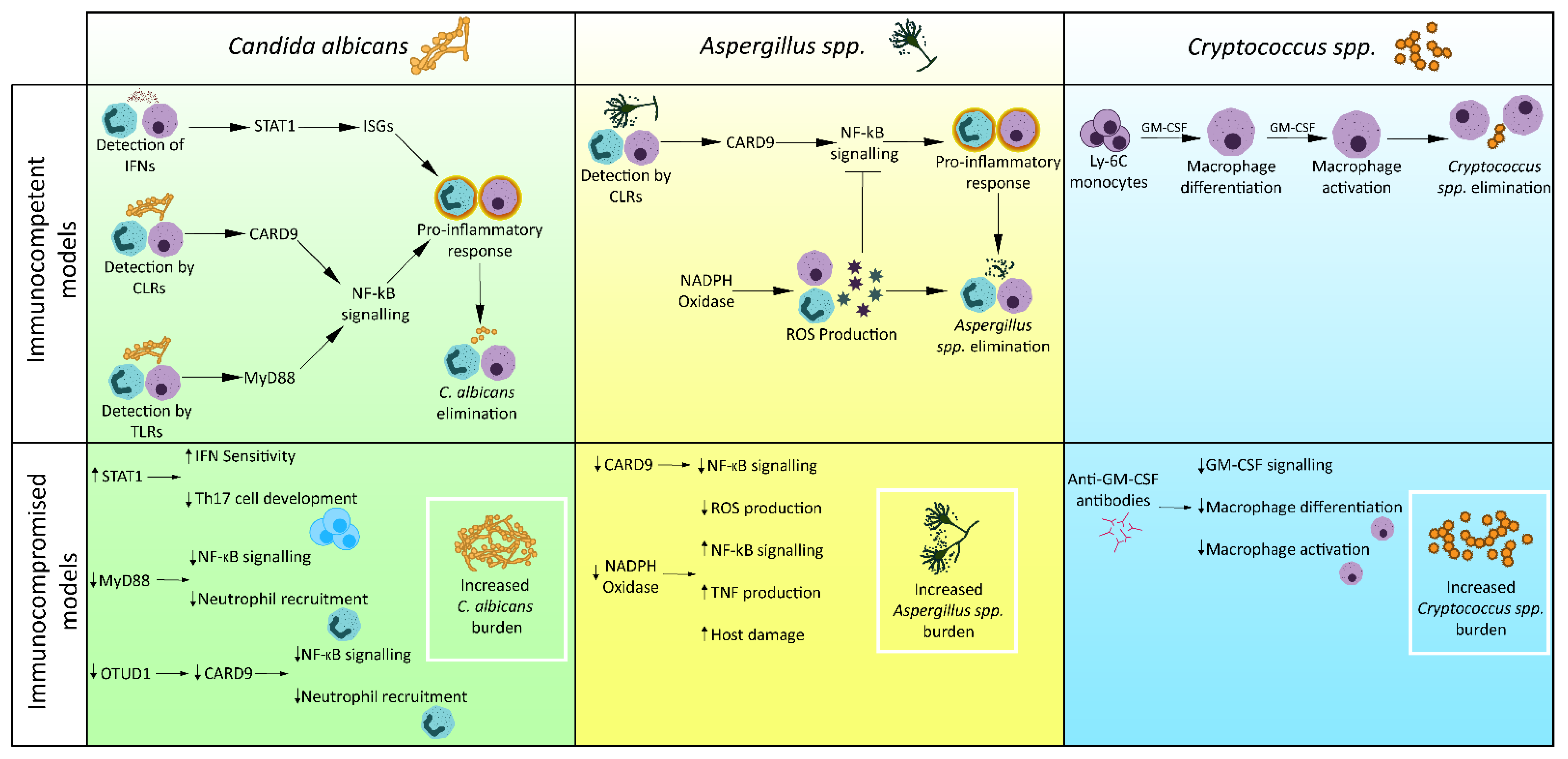
Frontiers | New Insights in Candida albicans Innate Immunity at the Mucosa: Toxins, Epithelium, Metabolism, and Beyond

Effects of LL-37 and the main products of SAP-dependent degradation of... | Download Scientific Diagram

JoF | Free Full-Text | Repositioning Lopinavir, an HIV Protease Inhibitor, as a Promising Antifungal Drug: Lessons Learned from Candida albicans—In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches
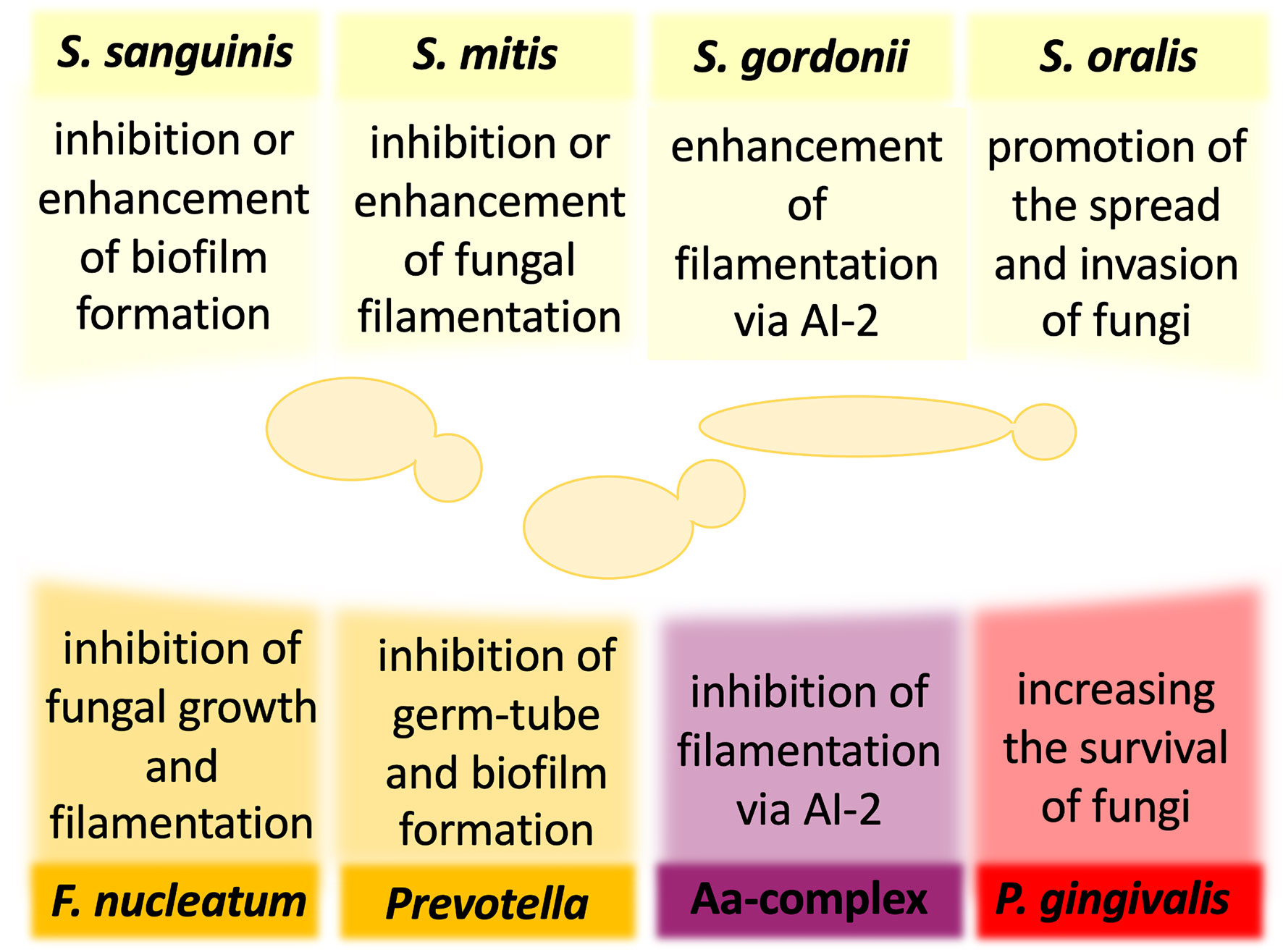
Frontiers | The Role of Candida albicans Virulence Factors in the Formation of Multispecies Biofilms With Bacterial Periodontal Pathogens

Aspartic Proteases and Major Cell Wall Components in Candida albicans Trigger the Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps | Semantic Scholar

Role of NAPDH oxidase in Sap-induced netosis. Neutrophils (2.2 × 10 5... | Download Scientific Diagram

Frontiers | Aspartic Proteases and Major Cell Wall Components in Candida albicans Trigger the Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
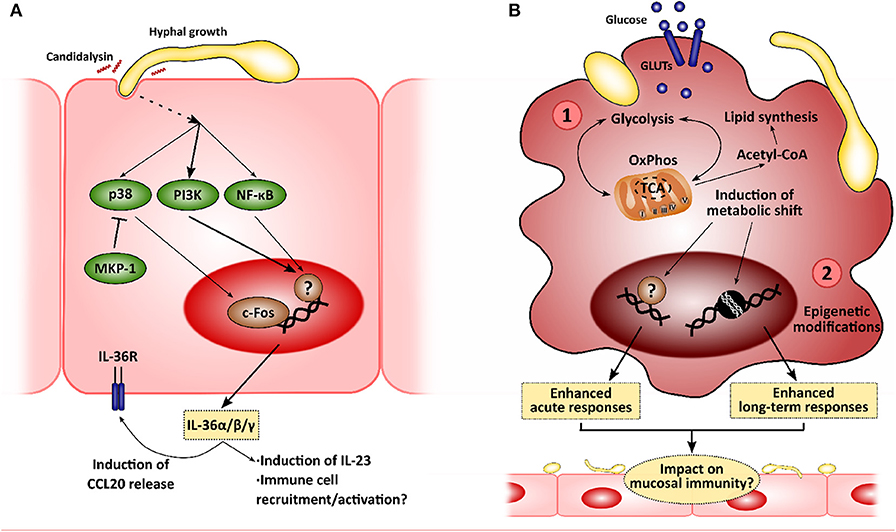
Frontiers | New Insights in Candida albicans Innate Immunity at the Mucosa: Toxins, Epithelium, Metabolism, and Beyond
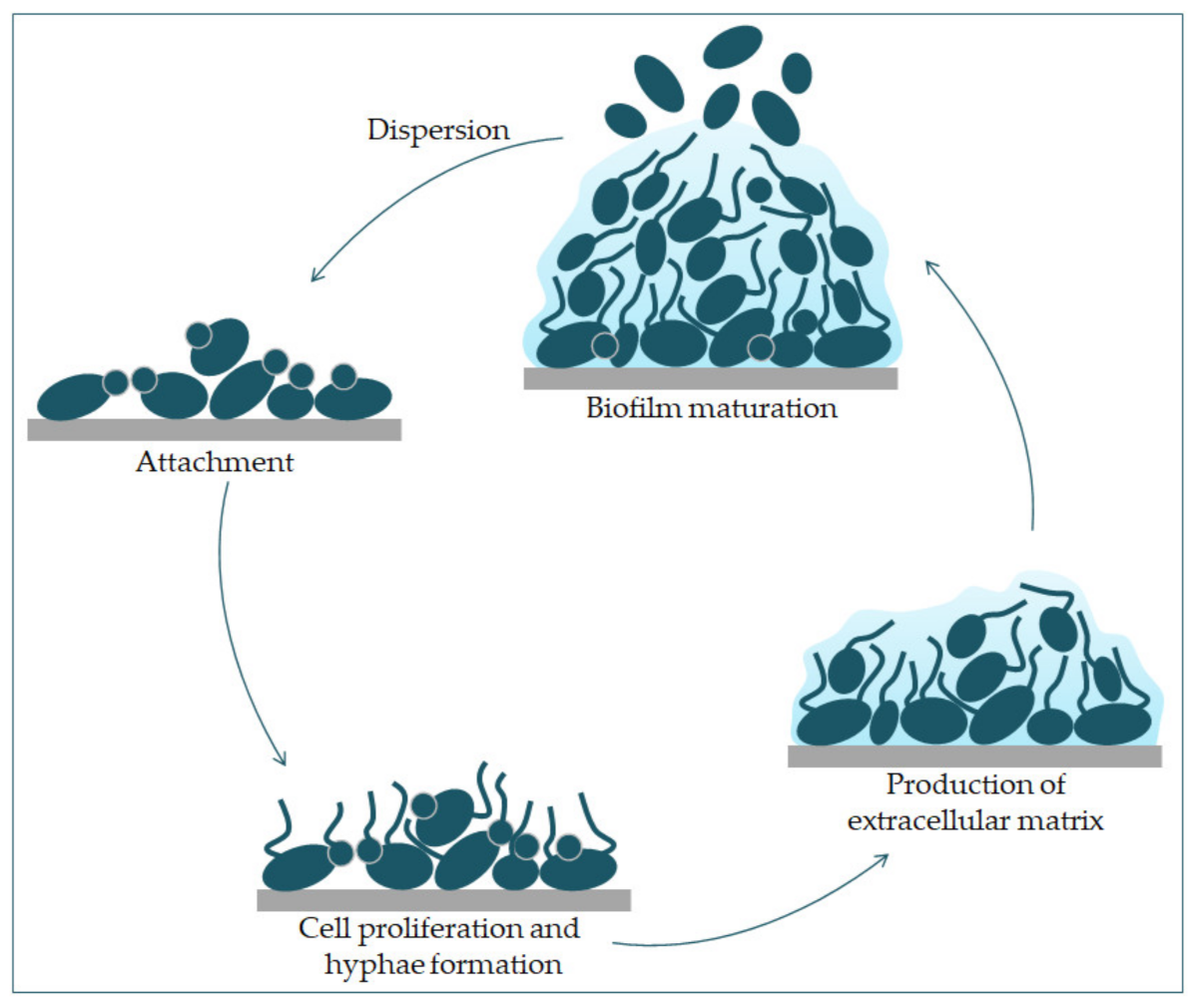
JoF | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans—The Virulence Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Infection
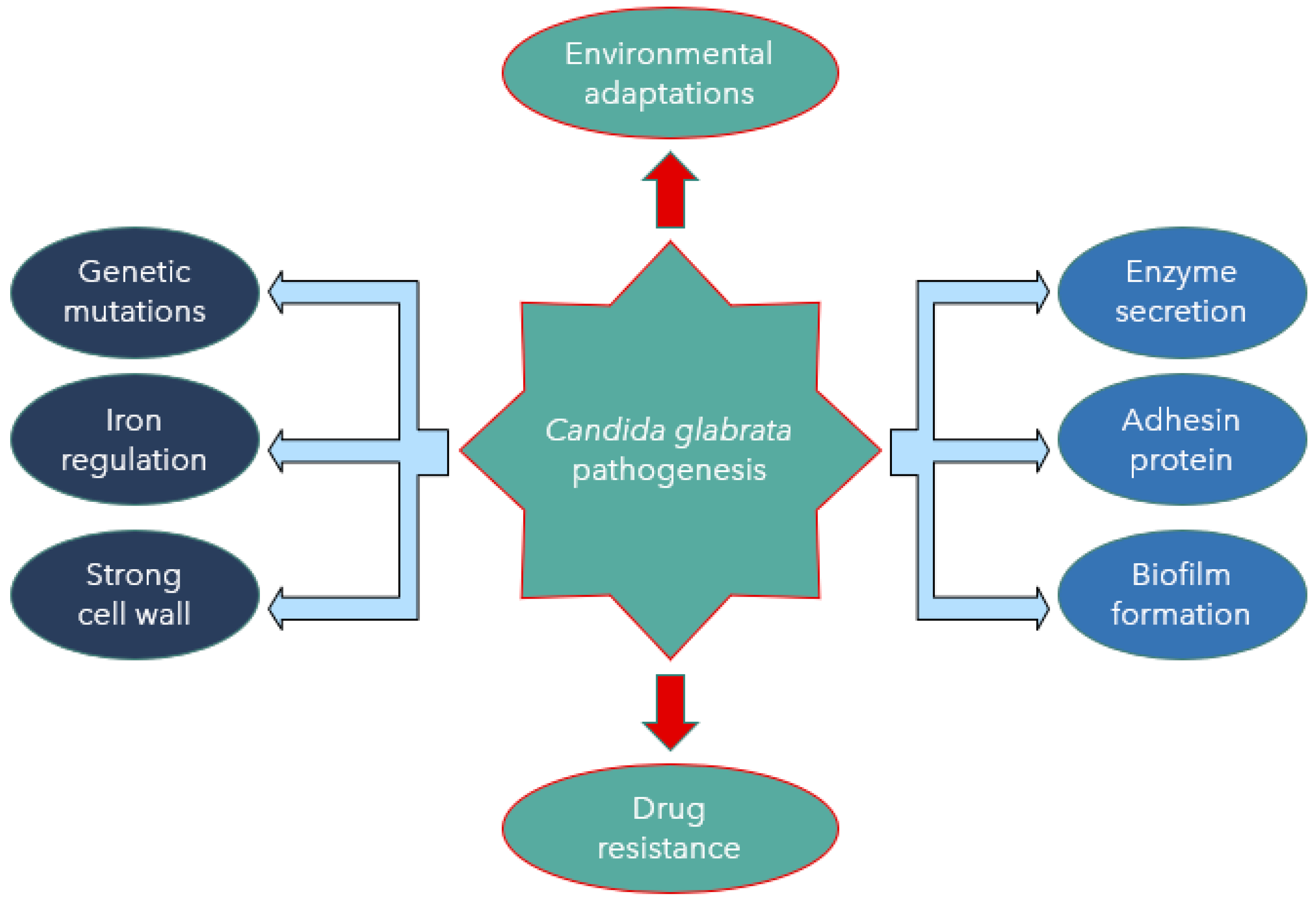
JoF | Free Full-Text | Candida glabrata: Pathogenicity and Resistance Mechanisms for Adaptation and Survival
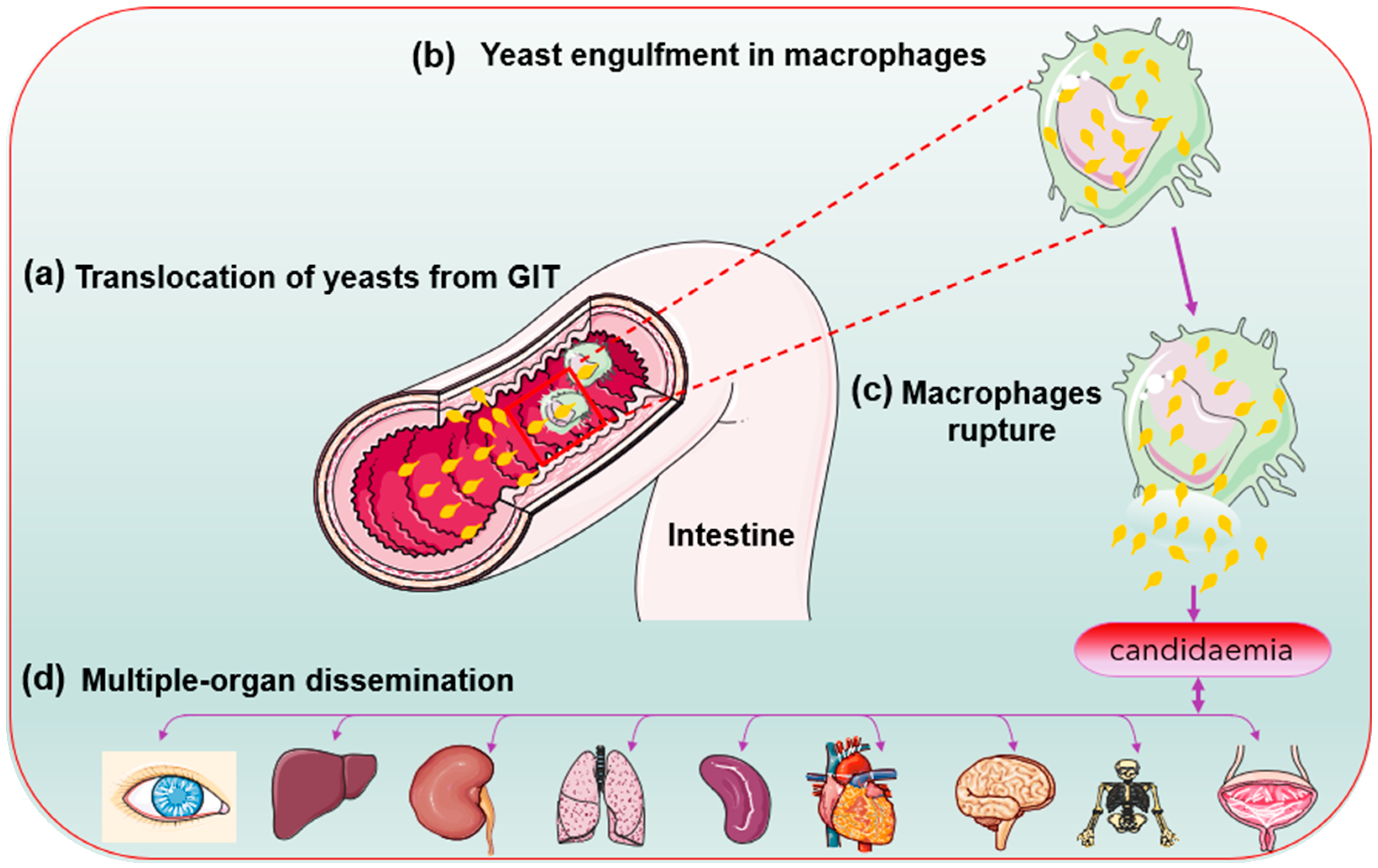
JoF | Free Full-Text | Candida glabrata: Pathogenicity and Resistance Mechanisms for Adaptation and Survival

Adhesive protein-mediated cross-talk between Candida albicans and Porphyromonas gingivalis in dual species biofilm protects the anaerobic bacterium in unfavorable oxic environment | Scientific Reports

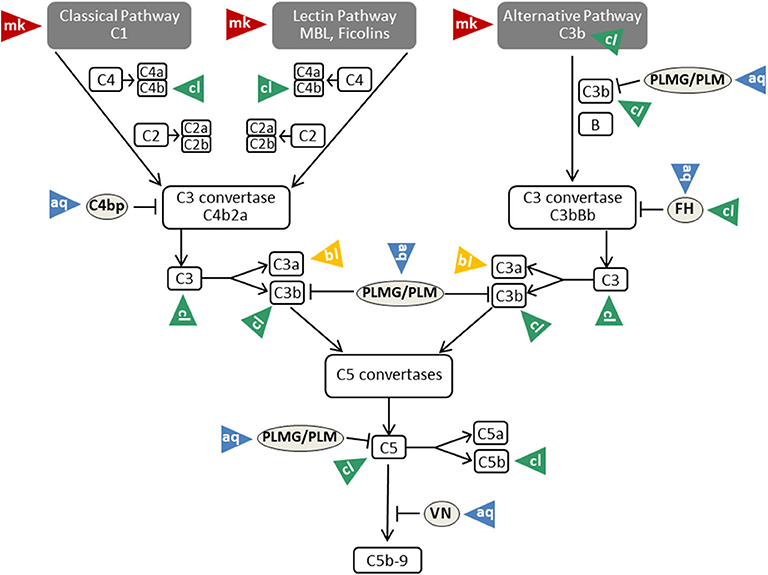
PDF) Kinin release from human kininogen by 10 aspartic proteases produced by pathogenic yeast Candida albicans

Cells | Free Full-Text | Proteinous Components of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Are Arrested by the Cell Wall Proteins of Candida albicans during Fungal Infection, and Can Be Used in the Host Invasion
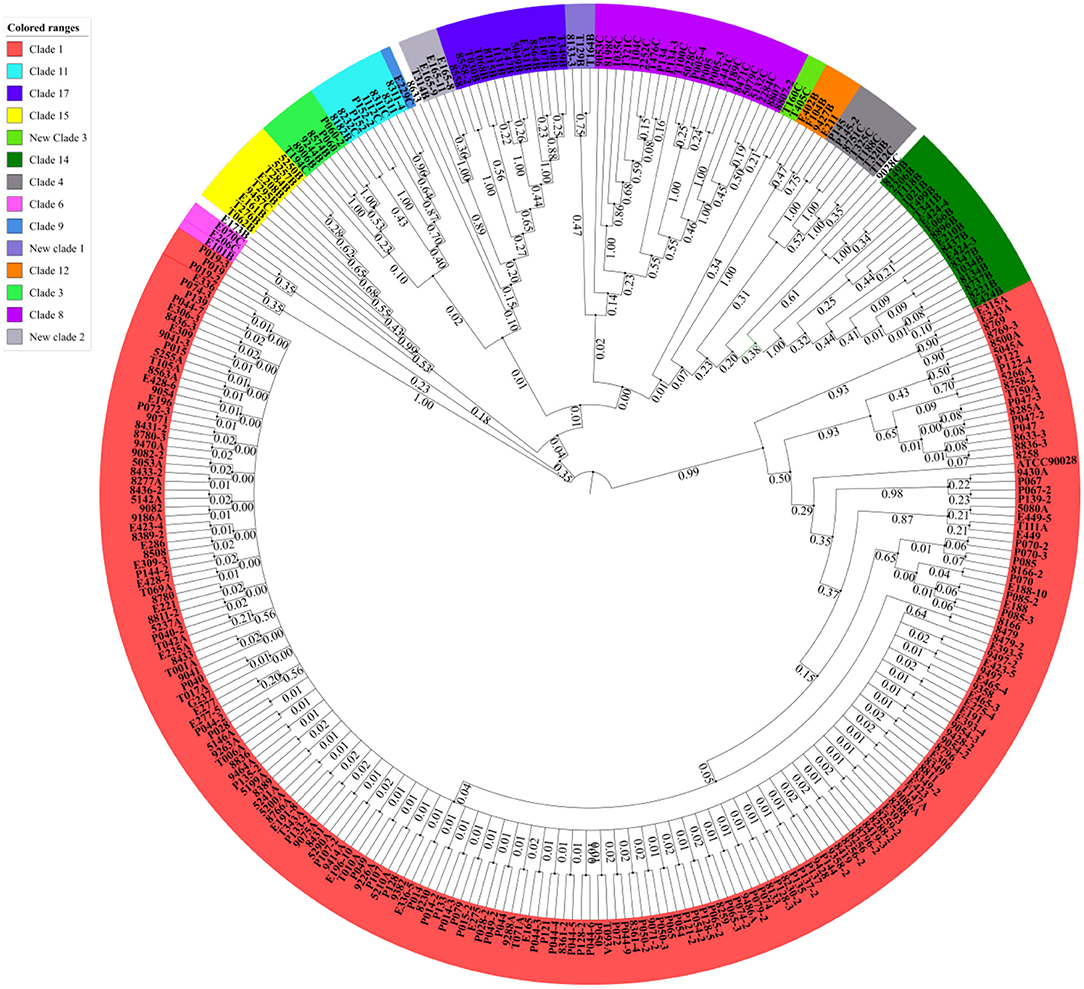
Frontiers | Candida albicans Multilocus Sequence Typing Clade I Contributes to the Clinical Phenotype of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis Patients

Inactivation of the antifungal and immunomodulatory properties of human cathelicidin LL-37 by aspartic proteases produced by the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. - Abstract - Europe PMC